
The Ultimate Guide to Intents and Entities in Chatbots for Smarter Customer Support

In today’s fast-moving digital world, AI customer service has become essential for businesses that want to keep customers happy. Companies increasingly rely on customer support automation to provide quick, personalized, and efficient responses. At the core of these systems are intents and entities in chatbot AI, which help a conversational AI truly understand what a user wants. Intents capture the purpose behind a message, while entities provide key details like dates, locations, product names, or preferences.
📑 Table of Contents
- The Ultimate Guide to Intents and Entities in Chatbots for Smarter Customer Support
- Key Highlights
- What are Chatbot Intents?
- What are Chatbot Entities?
- How Intent and Entities in Chatbots Work Together
- Types of Chatbot Intents
- Different Types of Entities in NLP
- Why Intents and Entities in Chatbots Matter
- Benefits of Using Intents and Entities in Chatbots
- Real-World Application
- Challenges and Limitations
- Process Intents and Entities in Chatbots
- Intent vs. Entity
- How to Train and Classify Chatbot Intents Step by Step
- Best Practices for Designing Intent-Driven Chatbots
- Future Trends in Chatbot AI
- Key Features of Chatboq.com
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Together, intents and entities in Chatbots enable conversational AI to offer real-time support, enhance customer satisfaction, and boost chatbot ROI. Proper implementation ensures that your digital assistant acts accurately and avoids limitations that could frustrate users. Tools like Chatboq enable businesses to implement intents and entities in chatbots system with no-code AI training, ensuring accurate, scalable, and intelligent support.
Key Highlights
| Intents define user goals in chatbots Entities provide context for accurate responses Combining intents and entities enables automation Chatbots improve customer support and satisfaction Future AI trends include emotional intelligence |
What are Chatbot Intents?
A chatbot intent is the goal a user wants to accomplish. Every interaction starts with an intent, whether it’s:
- Asking a question
- Making a purchase
- Scheduling an appointment
AI-powered chatbots use Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML) to understand many ways users express the same intent. This allows businesses to scale personalized interactions, improve Net Promoter Score (NPS), and handle complex queries through an AI-human hybrid model.
What are Chatbot Entities?
Entities provide the context that makes an intent actionable. While an intent like “Order a pizza” shows the goal, Entity Extraction identifies details such as size, toppings, and delivery location. With Knowledge Base Integration, chatbots deliver accurate response generation. Entities also power multilingual support and omnichannel support, enabling 24/7 availability, instant response times, and Sentiment Analysis. To guide proactive support or AI-Human Hybrid Model escalation when needed.
How Intent and Entities in Chatbots Work Together
When intents and entities in chatbots combine, chatbots can perform sophisticated actions. An example in e-commerce: a user types, “Show me blue sneakers in size 10 with free shipping.” The intent is product search, and entities are blue, size 10, and free shipping. This allows the AI Chatbot to filter products correctly, recommend options, and even offer promotions. Businesses using chatbot AI best practices often map intents and entities to workflows, ensuring consistent customer satisfaction (CSAT) improvement and call deflection.
These intents and entities in chatbots also support conversational AI commerce. Bots can process orders, schedule appointments, or answer questions automatically, leveraging Predictive Support and Proactive Support strategies. Companies can monitor metrics such as chatbot ROI and customer satisfaction (CSAT) improvement, while ensuring compliance and privacy safeguards.
Types of Chatbot Intents
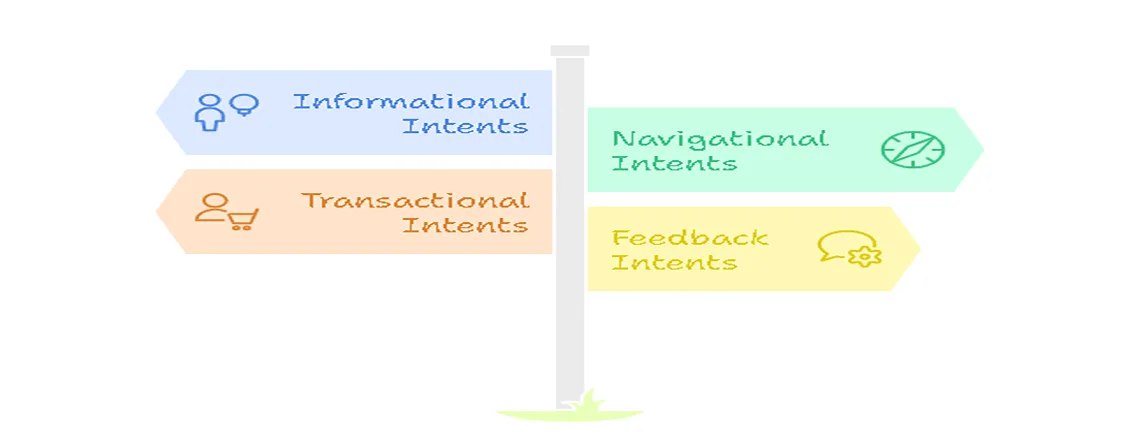
Informational Intents: Users seek knowledge, like “What are your business hours?” This supports AI customer service and improves speed.
Navigational Intents: Users want to find a resource, such as “Show me the return policy.” This enhances customer support automation.
Transactional Intents: Requests for actions, like “Order a large pepperoni pizza.” Vital for conversational AI commerce and 24/7 availability.
Feedback Intents: Users provide opinions, complaints, or ratings, like “Rate my experience.” Helps improve CSAT and Net Promoter Score (NPS).
Different Types of Entities in NLP
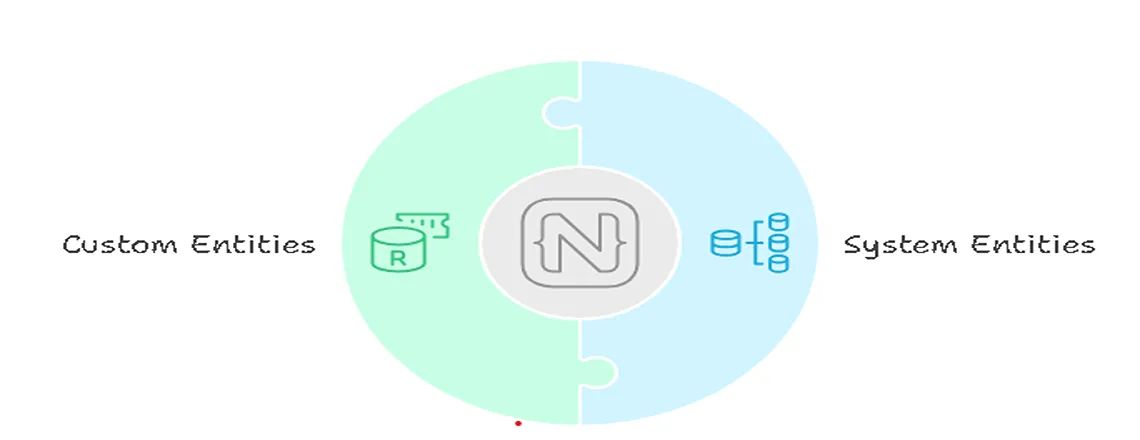
Entities give chatbots the details needed to execute an intent. They come in two main types:
System Entities: Predefined categories such as dates, times, numbers, and locations. For instance, “tomorrow” or “10 AM” in a booking request.
Custom Entities: Industry-specific data like product names, account numbers, or healthcare symptoms, enabling personalized chatbot interactions.
Example table:
| Industry | Example Query | Intent | Entity |
| Retail | Order Nike shoes size 10 | Purchase Intent | Product: Shoes, Size: 10 |
| Banking | Transfer $200 to savings | Transfer Intent | Amount: $200 |
| Travel | Book a flight to Miami | Booking Intent | Destination: Miami |
Why Intents and Entities in Chatbots Matter
Proper use of intents and entities in chatbots allows chatbots to deliver:
- Faster responses and 24/7 support
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Reduced workload for human agents
- Omnichannel support across platforms
- Data-driven insights for continuous optimization
Additionally, chatbots can perform sentiment analysis to detect frustration or satisfaction, further improving engagement.
Benefits of Using Intents and Entities in Chatbots
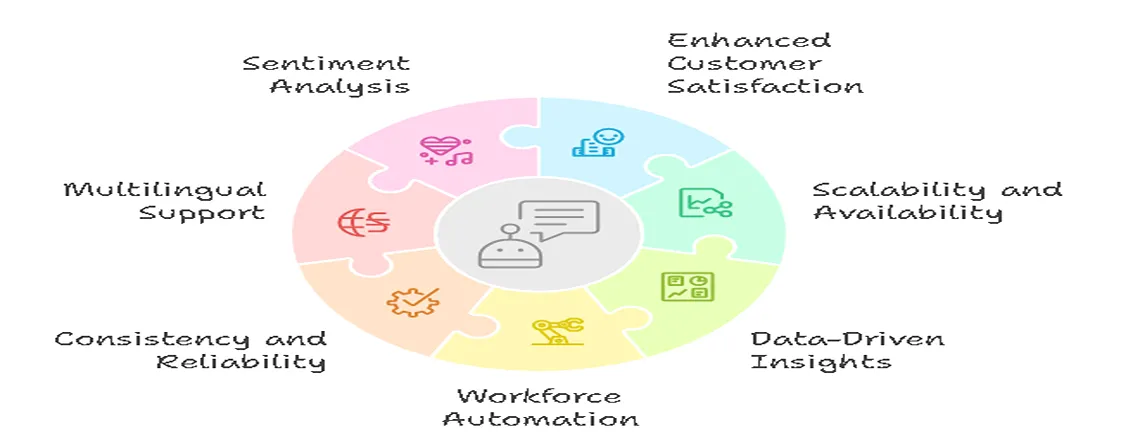
Properly implemented intents and entities in chatbots enable multiple business benefits. Chatbots with Continuous Learning AI customer service improve over time, reducing errors and increasing efficiency. Using Data-driven Insights, companies can refine their chatbot optimization, identify chatbot adoption challenges, and predict future trends. In addition, Digital Twins of Human Agents allow bots to mimic top-performing human interactions, delivering personalized interactions across omnichannel support environments.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Faster answers and personalized interactions improve CSAT.
- Scalability and Availability: Provides 24/7 availability without extra staff.
- Data-Driven Insights: Analyze user behavior and optimize services.
- Workforce Automation: Human agents focus on complex tasks while bots handle routine queries.
- Consistency and Reliability: Uniform messaging across channels ensures trust.
- Multilingual Support: Multilingual chatbots help global engagement and compliance.
- Sentiment Analysis: Detects emotions and escalates issues appropriately
With Chatboq, companies can maximize these benefits through CRM integration and no-code AI training.
Real-World Application
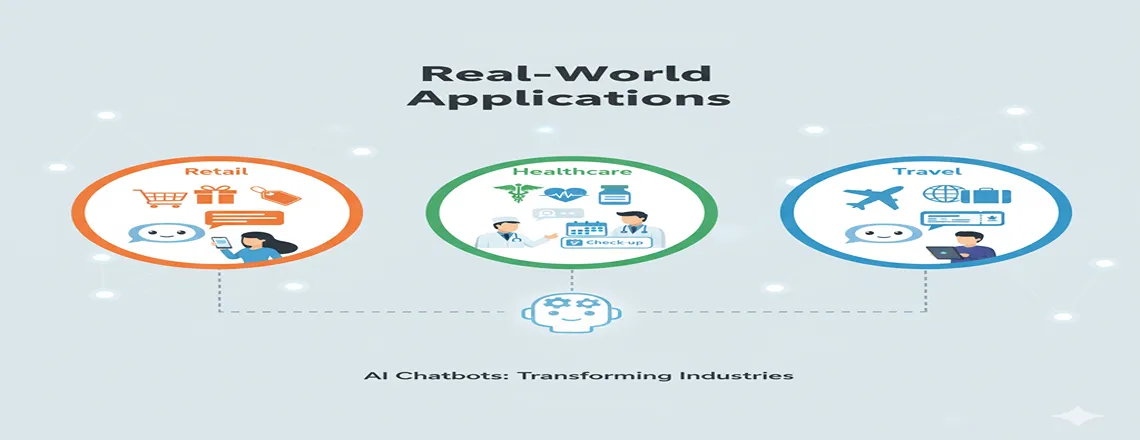
Businesses are leveraging intents and entities in chatbots to make customer interactions faster and more personalized.
- Retail: A chatbot can detect the intent “track order” and the entity “Order #4567,” instantly providing real-time shipment updates without human intervention.
- Healthcare: For scheduling purposes, the bot recognizes the intent “schedule appointment” and the entity “next Monday,” helping patients book appointments efficiently.
- Travel: When a user searches “Find flights to New York,” the bot combines the booking intent with the entity “New York,” offering relevant flight options immediately.
Case Study: A U.S. airline integrated predictive support and emotional AI into its chatbot system. The bots detected frustrated tones in customers’ messages, proactively offered rebooking options, and reduced call volumes by 30%, significantly boosting overall customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Limitations

Even with advanced AI, bots face limitations:
- Complex Queries: Misinterpret sarcasm, slang, or multi-step requests.
- Trust and Privacy Concerns: Sensitive data requires strong chatbot data privacy and ethical AI practices.
- Integration Complexity: Combining with legacy systems and chatbot integration with CRM can be challenging.
- Customer Adoption Challenges: Some users prefer human agents for complex interactions.
- Cultural and Language Nuances: Misinterpretations can affect omnichannel support in diverse regions.
Process Intents and Entities in Chatbots
Intents and Entities in Chatbots analyze queries, which are the phrases or words users use to express intent. For instance, “Track my order” and “Where’s my package?” indicate the same intent. Once identified, the bot extracts entities and performs the necessary action.
If the query is complex, chatbot AI escalation to human agents ensures uninterrupted support. By integrating with CRM systems and self-service knowledge bases, chatbots can continuously learn and deliver smarter, real-time assistance.
Intent vs. Entity
Intents focus on why a user interacts, while entities focus on what details are involved. For example, in “Book me a hotel in Miami,” the intent is hotel booking, and the entity is “Miami.”
A bot with strong intent recognition but weak entity extraction may misinterpret requests, frustrating customers. Combining both ensures accurate, personalized interactions, improves AI-powered chatbot self-service, and supports omnichannel support.
How to Train and Classify Chatbot Intents Step by Step
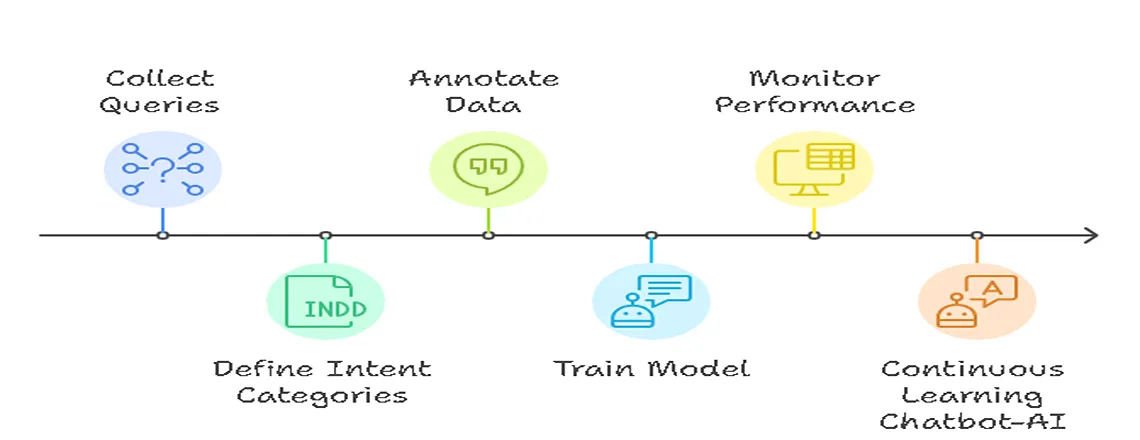
- Collect Queries: Gather phrases that represent user intent.
- Define Intent Categories: Categorize into informational, transactional, navigational, or feedback.
- Annotate Data: Mark entities within utterances.
- Train ML Models: Feed data into Machine Learning (ML) for intent recognition.
- Monitor Performance: Track error rates, misclassifications, and improve sentiment analysis.
- Continuous Learning Chatbot-AI: Update models regularly to improve chatbot optimization and real-time support.
Best Practices for Designing Intent-Driven Chatbots

- Start Small: Begin with a limited number of intents and expand gradually.
- Smooth Escalation: Always include chatbot escalation to a human agent for complex requests.
- Multilingual Support: Ensure global engagement with multilingual chatbots.
- CRM Integration: Connect bots to CRM for data-driven insights.
- Self-Service Knowledge Base: Enable users to find answers independently.
- Voice-Enabled Chatbots: Expand accessibility with voice-enabled chatbots.
- Hybrid Customer Service Model: Implement hybrid AI-human models to improve customer experience (CX).
Chatboq supports all these practices with easy-to-use AI training tools.
Future Trends in Chatbot AI
- Emotional AI: Bots will detect emotions and respond empathetically.
- Predictive Support: Anticipate customer needs before they ask.
- Proactive Support: Initiate helpful suggestions during user journeys.
- Digital Twins of Human Agents: Replicate top agent skills for consistency.
- Ethical AI: Ensure fairness, transparency, and chatbot data privacy compliance.
Key Features of Chatboq.com

- No-Code AI Training: Build intelligent chatbots without coding.
- CRM Integration: Seamlessly connect with existing systems.
- Omnichannel Support: Engage customers across web, chat, email, and social.
- Real-Time Analytics: Measure chatbot ROI and user satisfaction.
- Custom Entity and Intent Management: Handle industry-specific queries efficiently.
- Hybrid AI-Human Model: Escalate complex issues to human agents.
- Multilingual and Sentiment Analysis: Improve global engagement.
Conclusion
Intents and entities in chatbots are the backbone of conversational AI. Together, they allow chatbots to deliver faster, smarter, and more personalized support while saving time and reducing errors. For businesses, especially in SaaS, e-commerce, travel, and finance, embracing intents and entities means improved customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and scalable growth.
Start building your AI-powered chatbot with Chatboq today and deliver personalized, 24/7 support and elevate customer engagement.


Leave A Comment