
6 Different Types of Chatbots: Classification, Features & Examples
Customer service is always working. On holidays, during lunch breaks, even at two in the morning, they demand prompt responses. For businesses, meeting this demand without overloading human agents is a challenge.
📑 Table of Contents
- 6 Different Types of Chatbots: Classification, Features & Examples
- Key Highlights
- What is an AI Chatbot? How It Works
- Why Classifying Chatbots Matters for Businesses
- How Chatbots are Classified
- 6 Different Types of Chatbots
- Real-World Use Cases & Best Chatbot Examples
- How to Choose the Right Type for Your Business
- Implementation Tips & Best Practices
- Trends & Future of Chatbots
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Chatbot resolves these issues. These AI-powered customer support tools work 24/7 to answer inquiries, boost sales, and resolve problems efficiently. Modern conversational AI chatbots learn from interactions over time, improving accuracy and reducing support costs by up to 30%. Conversational AI is used by others to learn from interactions and adjust over time.
Discover the 6 different types of chatbots. You will learn about AI chatbots from well-known companies. You’ll also discover which business chatbot best suits your requirements.
Key Highlights
| Explore six main types of chatbots Compare chatbot features, pros, and limitations Learn real-world chatbot use cases Discover how to choose the right chatbot Understand future chatbot trends and innovation. |
What is an AI Chatbot? How It Works
A chatbot is a tool that communicates with customers using artificial intelligence (AI) and human-like language. Modern AI chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) to understand context and user intent. This makes interactions more natural, engaging, and effective at solving customer problems.
Why Classifying Chatbots Matters for Businesses
Choosing the right chatbot for your business that matches your needs is very important. Many businesses jump blindly into business automation without knowing their options. Many companies explore chatbot trends, but tailoring the choice to their specific needs brings the best results.
Classifying chatbots helps you find which chatbots match your business needs. Here’s why understanding types of AI chatbots matters:
- Saves money – No overpaying for features you don’t need
- Improves accuracy – The Right type means better answers
- Speeds deployment – Clear requirements lead to faster setup
- Plan growth – Start simple, upgrade as needs grow
Understanding chatbot use cases helps reduce costly mistakes and frustrating user experiences.
How Chatbots are Classified
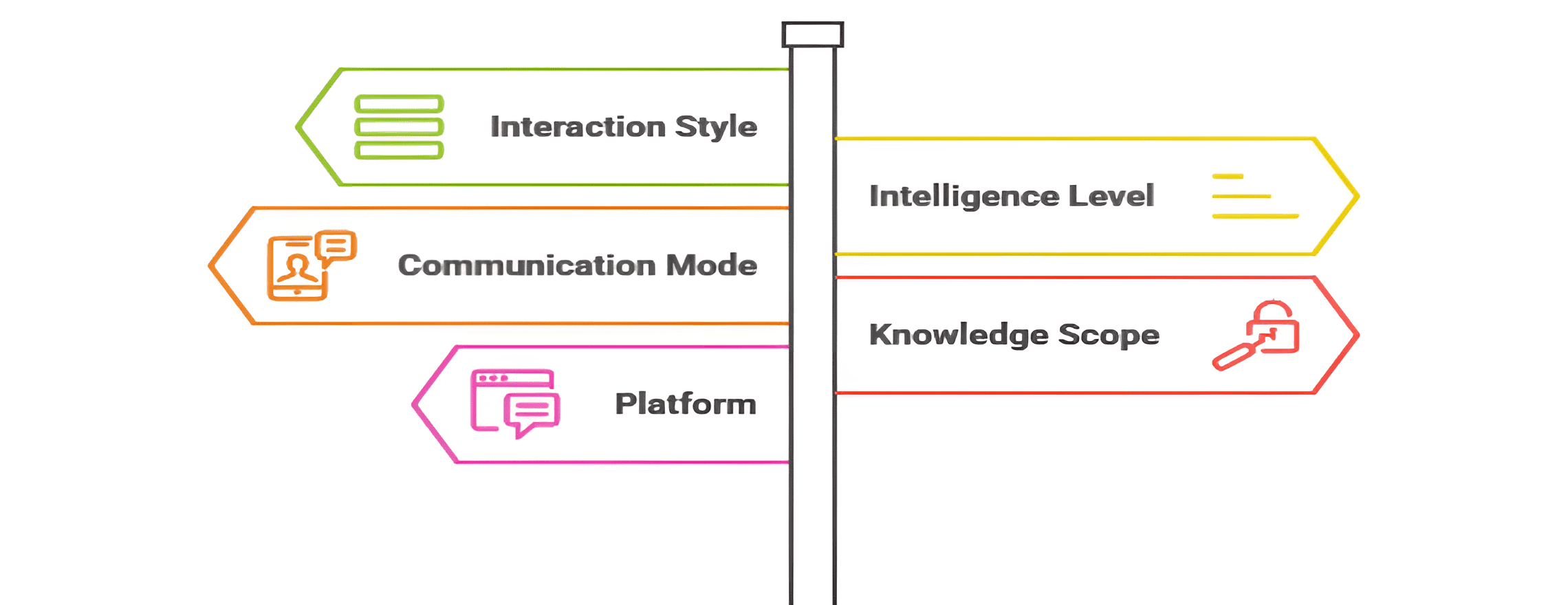
Different types of chatbots vary in several ways. Understanding these differences helps you choose correctly.
Interaction Style
- Menu/Button-based: Click options, predictable paths.
- Conversational AI: Free-form queries, natural language.
Intelligence Level
- Rule-based: Scripted responses, keyword-driven.
- AI-powered: Machine learning (ML) and NLP.
- Hybrid: Combines rules and AI.
Communication Mode
- Text chatbots: Web, app, and messaging.
- Voice assistants: Hands-free, spoken commands.
Knowledge Scope
- Closed-domain: Specialized tasks like banking or pizza orders
- Open-domain: General queries, less depth
Platform
- Website chatbots: Engage visitors online
- App chatbots: Inside mobile applications
- Voice assistants: Smart speakers and in-car systems
6 Different Types of Chatbots
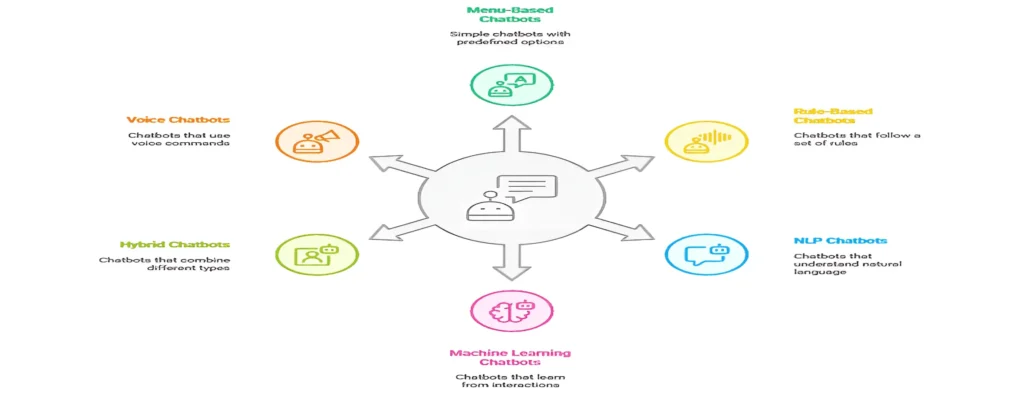
Chatbots can be classified in many ways. Here we’ll focus on six key types that are most widely used today. You will learn about the different types of chatbots, their pros & cons, and their various use cases. It will provide you with a complete understanding of chatbot classification. This will help you choose the chatbot type you need for your business.
1. Menu / Button-Based Chatbots
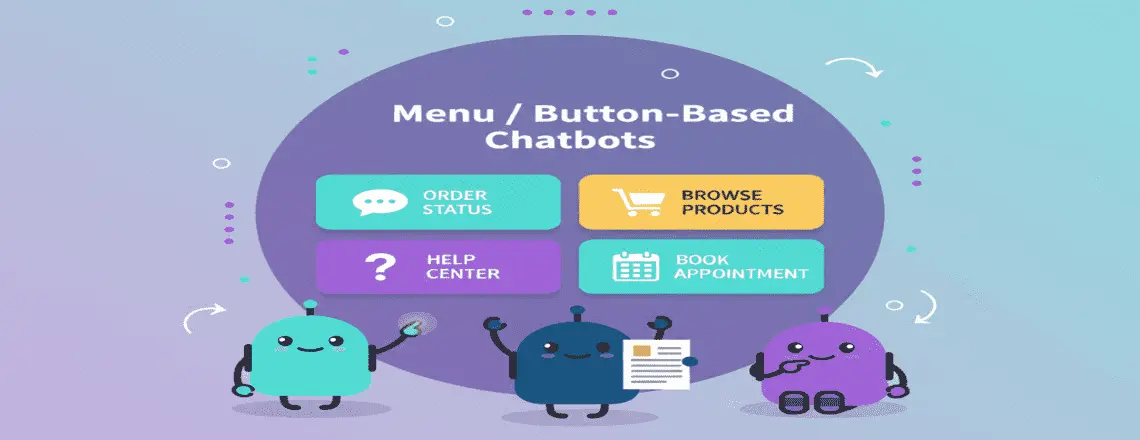
This is the simplest type of chatbot for businesses. Users click buttons or menus to navigate, like an interactive FAQ. You just select an option, and the bot shows the next step with no typing needed. It works best when customer questions are predictable.
Pros:
- Easy to build with basic chatbot tools
- Perfect for simple, predictable queries
- Works without training data
- Clear user guidance
Cons:
- Limited flexibility
- Can’t handle complex questions
- Requires many clicks for deep information
- Frustrates users with specific needs
Real Chatbot Examples:
Domino’s Pizza uses button-based ordering on Facebook Messenger. Users select size, toppings, and delivery options through menus.
Sephora’s chatbot on Kik guides makeup selection through visual menus and product categories.
Best Chatbot Use Cases:
- Food ordering and delivery
- Appointment scheduling
- Product catalogs with clear categories
- Simple customer service for common questions
2. Rule-Based Chatbots

Rule-based chatbots follow predefined flows using simple if-then logic. They’re more flexible than menu bots but still controlled. The bot looks for keywords or phrases and responds with programmed answers. For example, if a user types “hours,” it displays the store’s timings. If the input doesn’t match any rule, it gives a fallback message or hands off to a human. This works best for predictable questions that don’t need advanced language understanding.
Pros:
- Predictable and reliable
- Complete control over conversation flows
- No training data needed
- Fast to deploy for specific tasks
Cons:
- Can’t understand variations in phrasing
- Breaks when users ask unexpected questions
- Requires manual updates for new scenarios
- Limited to pre-programmed knowledge
Real Chatbot Examples:
The IRS uses rule-based bots to help taxpayers find forms and deadlines. Users type keywords like “refund” or “extension.”
Subway’s chatbot for customer service on Messenger uses rules to guide sandwich customization and placing orders.
Best Chatbot Use Cases:
- FAQ automation
- Form filling and data collection
- Simple transactions (bill payments, balance checks)
- Lead qualification with structured questions
3. NLP / Intent-Based Chatbots
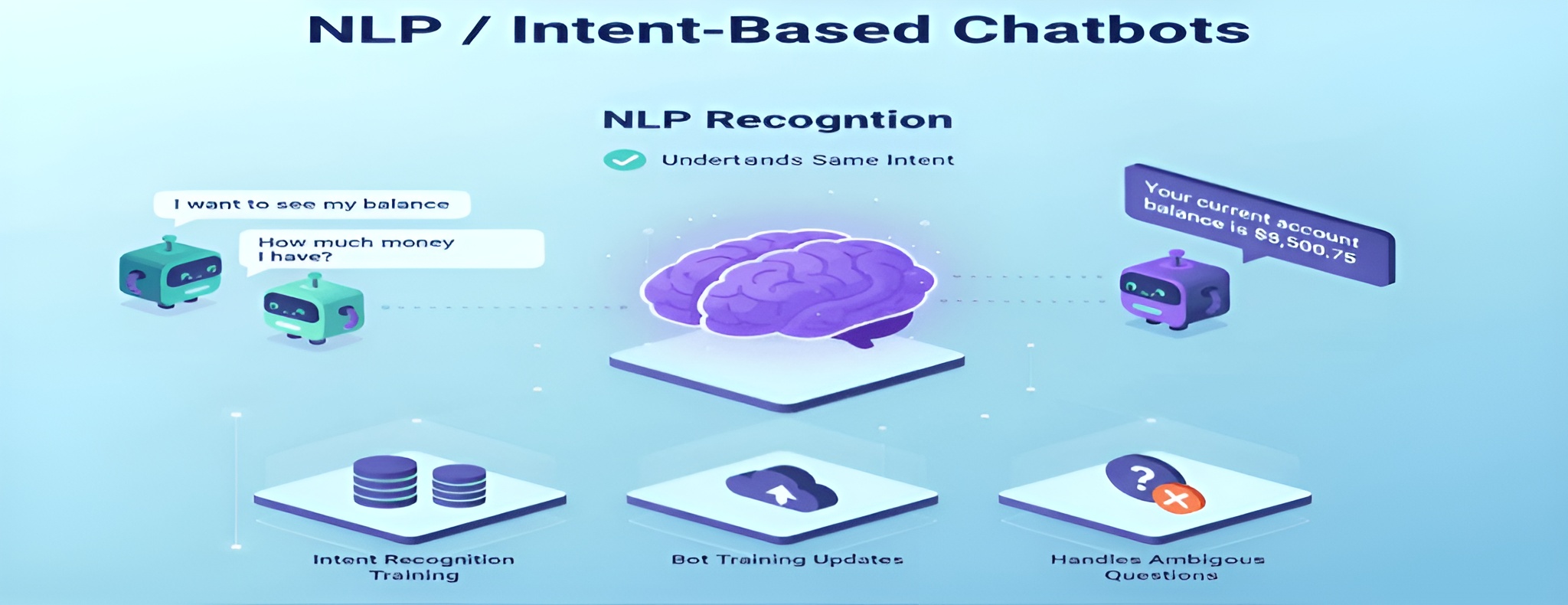
AI-powered chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) to understand user intent, not just keywords. They can recognize that “I want to see my balance” and “How much money do I have?” mean the same thing. They analyze context and sentence structure to provide more natural, human-like responses. This makes automated customer service smoother and less frustrating.
Pros:
- Understands conversational AI patterns
- Handles phrasing variations
- Feels more human-like
- Reduces customer engagement friction
Cons:
- Requires intent recognition training
- Needs regular bot training updates
- Can misinterpret ambiguous questions
- More complex than rule-based chatbot platforms
Real AI Chatbot Examples:
Bank of America’s Erica uses NLP to help customers check balances, transfer money, and find transactions through conversational queries.
H&M’s chatbot for apps understands fashion preferences described in natural language and suggests matching outfits.
Best Chatbot Use Cases:
- Customer support automation with varied questions
- Banking and financial services
- Travel booking and changes
- E-commerce product search
4. Machine Learning / Contextual Chatbots
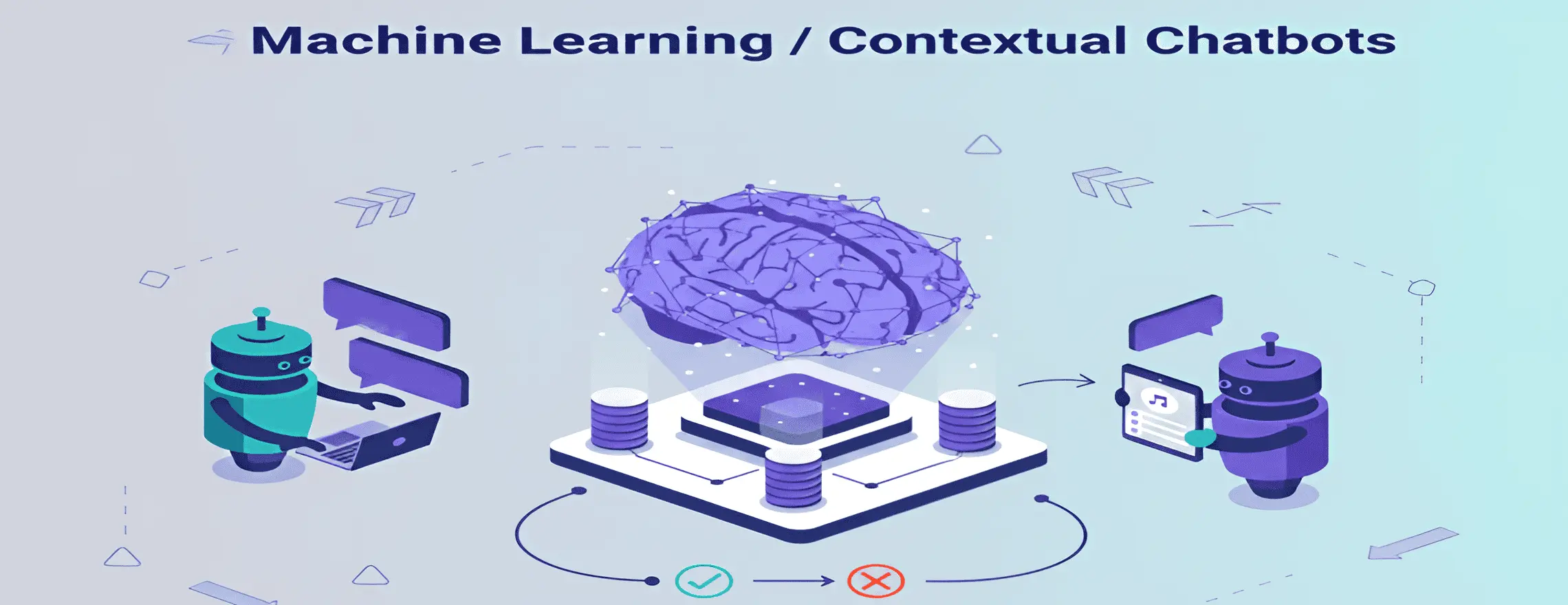
Contextual chatbots use machine learning (ML) to learn from past conversations and improve over time. They remember previous messages, maintain multi-turn dialogues, and adapt responses based on patterns and user feedback. This makes them smarter with every interaction, ideal for handling complex or unpredictable customer queries.
Pros:
- Improves automatically with model training
- Remembers conversation context
- Handles complex, multi-turn dialogues
- Personalizes responses based on user history
Cons:
- Needs large training datasets
- Requires ongoing chatbot analytics monitoring
- Can produce unexpected responses
- More expensive to develop and maintain
Real AI Chatbot Examples:
Google Assistant keeps track of your previous questions. Ask, “What’s the weather?” then follow up with, “How about tomorrow?” and it understands the context.
Spotify’s virtual assistant learns your likes and suggests playlists based on what you’ve listened to and your feedback.
Best Chatbot Use Cases:
- Technical support requiring troubleshooting
- Healthcare symptom assessment
- Complex booking systems
- Personal shopping assistants
5. Hybrid Chatbots

Hybrid chatbots mix rule-based logic and AI capabilities. They use rules for simple questions and AI for complex questions. This gives quick, predictable answers while handling tricky queries naturally. It’s a practical choice for businesses moving from basic to more advanced automation.
Pros:
- Best of both chatbot frameworks
- Reliable for common questions
- Flexible for uncommon scenarios
- Easier to manage than pure AI
Cons:
- More complex architecture
- Requires careful design of rule-AI handoff
- Still needs bot training data for the AI component
- Can feel inconsistent if poorly implemented
Real Chatbot Examples:
Mastercard’s chatbot handles simple balance checks with rules but uses AI for fraud detection discussions and complex dispute resolution.
Amtrak’s Julie bot uses rules for ticket booking basics and conversational AI for handling schedule changes and special requests.
Best Chatbot Use Cases:
- Enterprise customer service
- Multi-function chatbot applications (sales + support + booking)
- Healthcare triage (rules for emergencies, AI for symptom analysis)
- Any scenario mixing simple and complex queries
6. Voice / Conversational Voice Chatbots
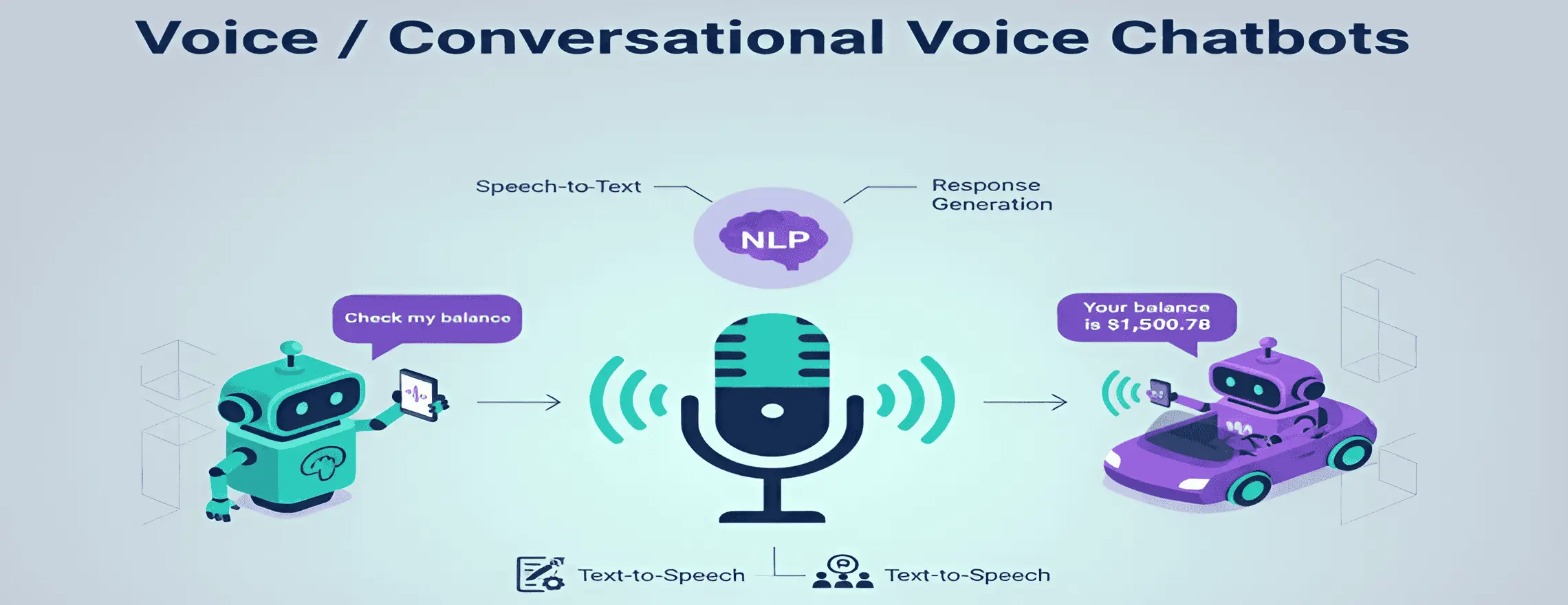
Voice assistants reply to voice commands using speech recognition and NLP. They convert your voice to text, understand your intent, generate a response, and speak it back to you instantly. This makes interactions feel natural and personal when typing isn’t suitable.
Pros:
- Hands-free operation
- Natural for phone-based automated customer service
- Accessible for users with reading difficulties
- Feels personal and immediate
Cons:
- Accent and background noise challenges
- Requires additional voice chatbot technology stack
- Harder to display visual information
- Privacy concerns with voice data
Real Chatbot Examples:
Amazon Alexa handles shopping, smart home control, and information queries through voice commands across multi-channel platforms.
Capital One’s Eno works through voice assistants to check balances and answer account questions using conversational AI.
Best Chatbot Use Cases:
- Smart home devices
- In-car virtual assistants
- Phone-based customer service automation
- Accessibility services for visually impaired users
Test Chatbot Demo
Comparison Table for 6 Different Types of Chatbots
| Type | Technology | Best For | Strengths | Limitations |
| Menu/Button | Button navigation | Simple tasks, product selection | Easy to use, no typing | Limited flexibility |
| Rule-Based | Keyword matching | FAQs, basic support | Predictable, fast setup | Can’t handle variations |
| NLP/Intent | Natural language processing | Customer service, search | Understands natural speech | Needs bot training |
| ML/Contextual | Machine learning, context memory | Complex support, personalization | Learns and improves | Requires large datasets |
| Hybrid | Rules + AI | Enterprise, multi-function | Balanced control & flexibility | Complex architecture |
| Voice | Speech recognition, TTS | Phone service, smart devices | Hands-free, accessible | Background noise issues |
See how Chatboq combines all 6 types in one platform
Real-World Use Cases & Best Chatbot Examples

Chatboq Platform
Chatboq offers a complete chatbot platform that brings together different types of chatbots in one place. The platform works with both text and voice assistants, making it a true hybrid chatbot for business needs with support for many channels. Chatboq’s chatbot analytics dashboard tracks conversation flow success rates and highlights areas for improvement. The platform enables smooth chatbot integration with popular CRM systems, helpdesk software, and payment processors through API integration. This makes it one of the best chatbot platforms for businesses seeking customer support automation without extensive development resources.
Explore how Chatboq handles hybrid chatbots today.
E-Commerce
Sephora’s chatbot boosted makeover bookings by 11% on Kik by asking preferences and scheduling in-store appointments, showing strong customer engagement.
eBay’s ShopBot helps users find products using conversational AI, handling vague requests like “something cool for my dad,” highlighting advanced natural language processing.
Banking & Finance
Bank of America’s Erica served 1 billion client requests by 2021. It handles balance checks, bill payments, and spending insights through conversational AI.
Wells Fargo’s chatbot for customer service resolves 90% of common inquiries without human handoff. Topics include card activation, passwords, and transaction disputes.
Healthcare
Babylon Health’s AI chatbot examples include symptom triage and doctor appointment booking. It serves over 4 million users across multiple countries through business automation.
Woebot provides mental health support through daily check-ins using contextual chatbots. Clinical studies show it reduces depression symptoms by 13-28%.
Travel & Hospitality
Hilton’s Connie robot assists hotel guests with local recommendations. It uses Watson AI to understand questions and suggest attractions through natural language processing.
KLM handles 15,000 customer questions weekly through social media chatbots on multi-channel platforms. Response time dropped to under 10 minutes.
Customer Support
Autodesk’s chatbot resolved 30,000+ support tickets in the first year. It freed human agents to handle complex technical issues through smart live chat escalation.
Lyft’s chatbot for apps helps riders track drivers and adjust pickup locations. It reduced support tickets by 20% in six months through automated customer service.
How to Choose the Right Type for Your Business
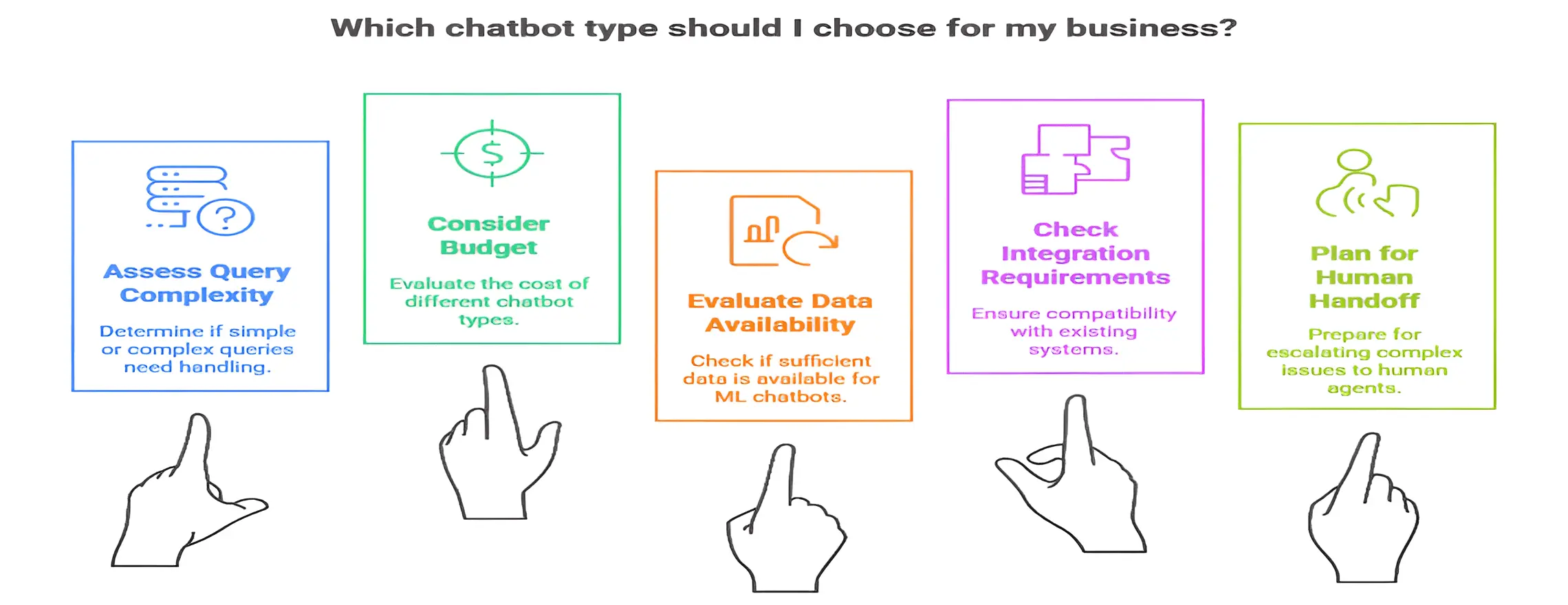
Choosing the right chatbot requires thought. Start simple and expand as needed. Consider your customer questions, interaction channels, and technical resources. You need to make sure the chatbot integrates with your CRM, helpdesk, and databases.
Step 1: Assess Query Complexity
- For simple questions, a menu or rule-based bot is enough.
- For complex or varied queries, use NLP or machine learning (ML) chatbots.
- Consider if the bot needs to remember previous messages or if one-off answers are enough.
Step 2: Consider Your Budget
- Menu/Rule-based bots: $500–$5,000
- NLP chatbots: $5,000–$50,000
- ML/Contextual chatbots: $50,000–$500,000+
- Start small if your budget is tight, and upgrade later as needed.
Step 3: Evaluate Available Data
- ML chatbots need conversation history to learn effectively.
- If you don’t have past data, start with rule-based or NLP bots.
- Aim to collect 1,000–10,000 conversation samples for better intent recognition.
Step 4: Check Integration Requirements
- Will your bot need access to databases, CRMs, or payment systems?
- Make sure your platform supports API integration.
- Voice assistants require extra setup for speech services and phone systems.
Step 5: Plan for Human Handoff
- Ensure your bot can escalate tricky issues to human agents.
- Track escalation rates using chatbot analytics.
- If over 30% of chats are escalated, consider optimizing the bot for better responses.
Implementation Tips & Best Practices

Building a chatbot is only the beginning. Effective conversation design, consistent observation, and ongoing development are key to success. Focus on your top customer questions first, create natural, friendly dialog flows, and always offer human handoff options. Test thoroughly with your team and beta users, then review analytics weekly to fix confusing interactions and improve the bot over time.
Here are some best practices to follow:
- Design easy-to-follow conversation flows: Fix unclear paths, test with real users, and map user journeys.
- Improve how the bot understands questions: Put similar questions together and use many examples to teach the bot.
- Build smart fallback logic: Offer alternatives or human handoff instead of just saying “I don’t understand.”
- Track performance: Watch for finished conversations, how long it takes to solve problems, customer happiness, and how often chats are sent to a person.
- Keep teaching and updating the bot: Add new types of questions, update answers, and teach the bot again often.
- Multi-channel Support: Put it on websites, apps, and messaging tools, and make sure it remembers the conversation everywhere.
- Connect with business tools: Link the bot to customer management, helpdesk, payment, and calendar systems for more personal and accurate answers.
Chatbot platforms like Chatboq make these integrations straightforward with pre-built connectors and API integration support.
Get your free trial of Chatboq today and start automating customer support across web, app, and messaging platforms effortlessly.
Trends & Future of Chatbots

Chatbot technology is evolving fast, with generative AI and large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 leading the way. Modern chatbots combine text, voice, and visuals for richer interactions and can remember past conversations for personalized experiences.
Here are some key trends you need to know:
Generative AI & LLMs
The integration of generative AI and large language models represents a fundamental shift in how chatbots operate. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, these advanced models can generate human-like responses dynamically and handle nuanced questions without explicit training for every scenario.
Multimodal conversational AI
Today’s chatbots process multiple types of input simultaneously, including images, videos, audio, and text. This enables more natural interactions where customers can combine visual information with spoken or written queries for smarter, more comprehensive support.
Advanced context understanding
Modern chatbots maintain context across conversations, remember user preferences, and detect emotions in messages. This allows them to personalize responses, adjust their tone appropriately, and escalate complex issues to human agents when needed.
Adoption statistics
The chatbot market reached $5.1 billion in 2024 with 23% annual growth, and 67% of consumers have used chatbots for support. Millennials lead adoption at 88%, demonstrating that chatbots have become a standard, expected customer service channel.
ROI & cost benefits
Businesses report 70% lower service costs after implementing chatbots, with many achieving 300–400% ROI in the first year. These savings come from automating routine inquiries, enabling 24/7 support, and freeing human agents for high-value interactions.
Chatbots are becoming smarter, more personal, and multi-functional. Early adoption gives businesses a strong edge in customer support and engagement.
Conclusion
Chatbots have evolved from simple menus to AI-powered, learning bots. Start with a rule-based or NLP chatbot for common questions, focus on top customer needs, and refine using analytics. Expand gradually with clear dialog flows and multi-channel integration. Platforms like Chatboq make scaling easy. Successful bots, like Sephora’s and Bank of America’s, show faster responses, higher engagement, and lower costs. Start testing, learn what works, and grow your chatbot strategy.
Get your free trial of Chatboq and automate customer service across web, app, and messaging platforms.


Leave A Comment